INTRODUCTIONGlobal Stretching
Global Stretching is a different approach to muscular stretching: its correct application leads to enhanced motor skills and fine-tuned technical gestures.
A good theoretical knowledge of GS basics, good control skills and a good ability to listen to body reactions and signals, together with a specific goal to pursue, are all necessary elements related to successful results.
Correct execution of GS routines leads to relief for layers of muscle fibers from surrounding connective tissues, often acting like a restraining factor. Specifically, due to bad posture habits, traumas, scars and overloads (both functional and non-functional), tissue is likely to recede.
The overall benefits of the GS method are a greater proprioception, a lower exposure to injuries, a better muscular flexibility and more precise technical gestures. Moreover, a greater availability of muscular fibers translates into a greater potential strength to express.
Diving is related to a range of movements and standard positions where good joint mobility and healthy articular links are key factors. These movements can be performed and improved by Global Stretching postural exercises/routines.
PancaFit® is the key tool employed in Global Stretching, as athletes can easily mimic diving positions and, by way of taking advantage of antigravity, to apply Global Stretching at its highest levels and to the best results.
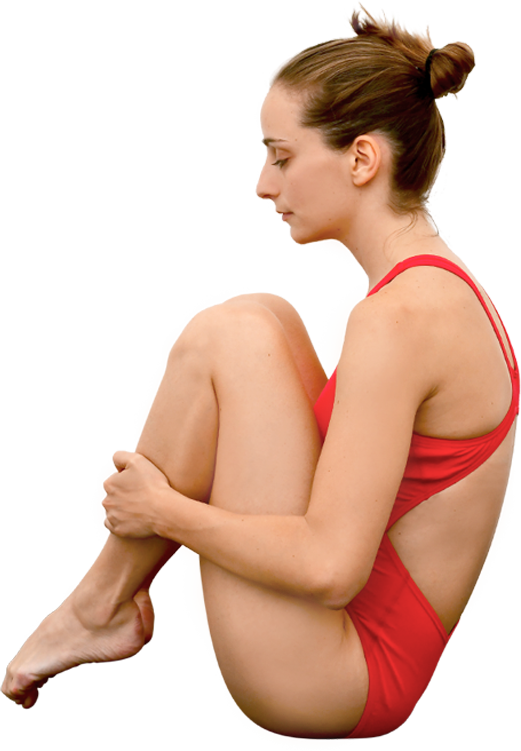

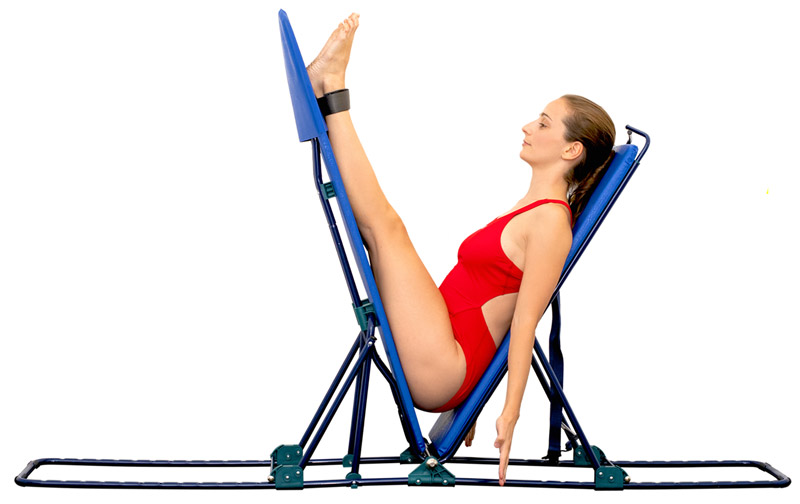
Tuck position
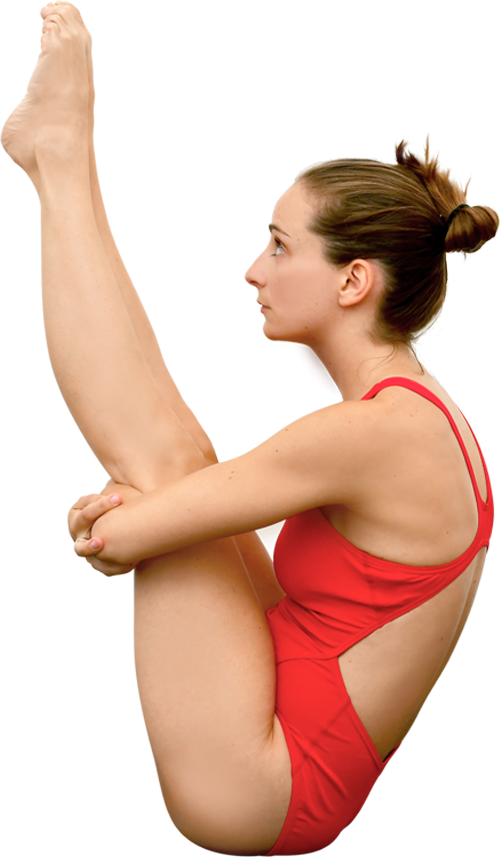

Pike position
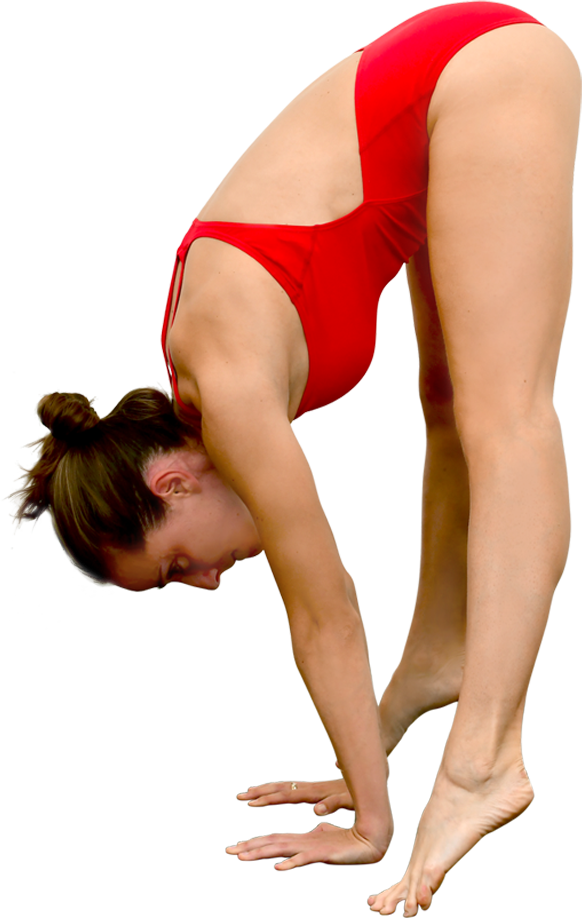

Pike position

Vertical Entry
Global Stretching Method Key Factors:
- Reference position
- Exact symmetry
- Body awareness
- Breathing control
- Stresses/strains management
- Stretching routines planning (short/long term)
Basic exercises:
- Diaphragmatic breathing
- Selective activation-deactivation of body areas
- Specific self-elongation/stretching
- Proprioceptive abdominals
THE TOOLPancafit®
Designed and created by Dr. Raggi in 1997, Pancafit® was conceived as a decompensated global muscular stretching method.
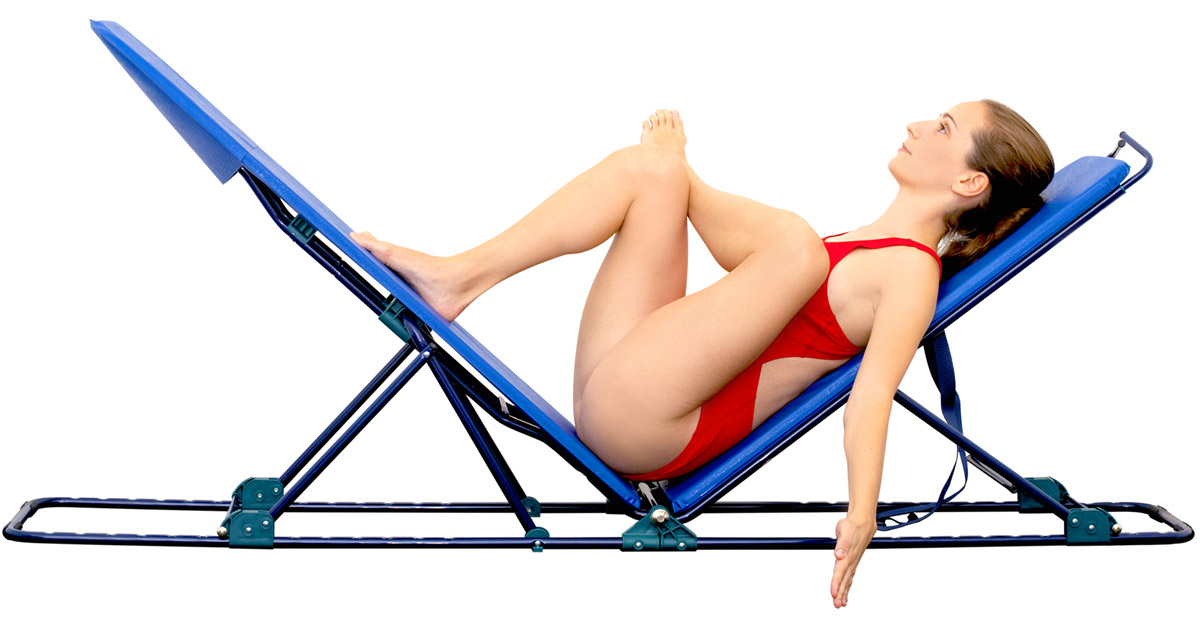
The tool consists of two boards connected by a metallic hinge. Each board can be vertically adjusted to different modular degrees. The peculiarity of the tool lies in the option to adjust the closing angle of thigh/torso and torso/thigh from 180 degrees to zero degrees.
This translates into back-chain elongation/stretching and replication of the pike position to narrower degrees.
The handles on top of the seatback allow to stretch and elongate upper limb muscles while maintaining an exact alignment with the torso, i.e. the arms are perfectly aligned to the body, thus improving verticality.
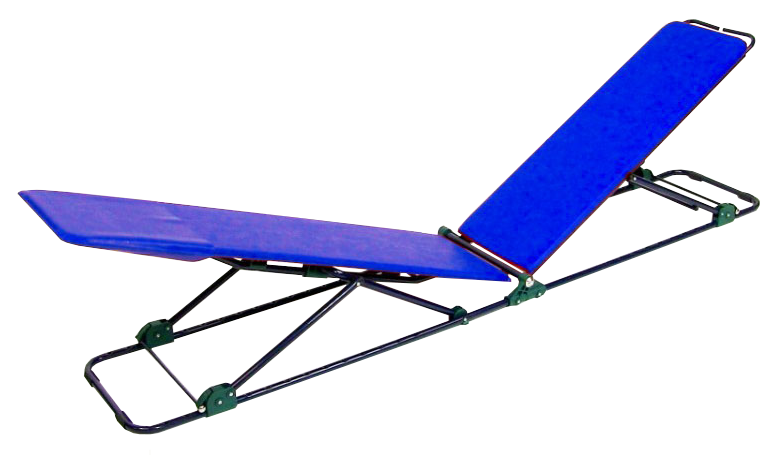
Pancafit®
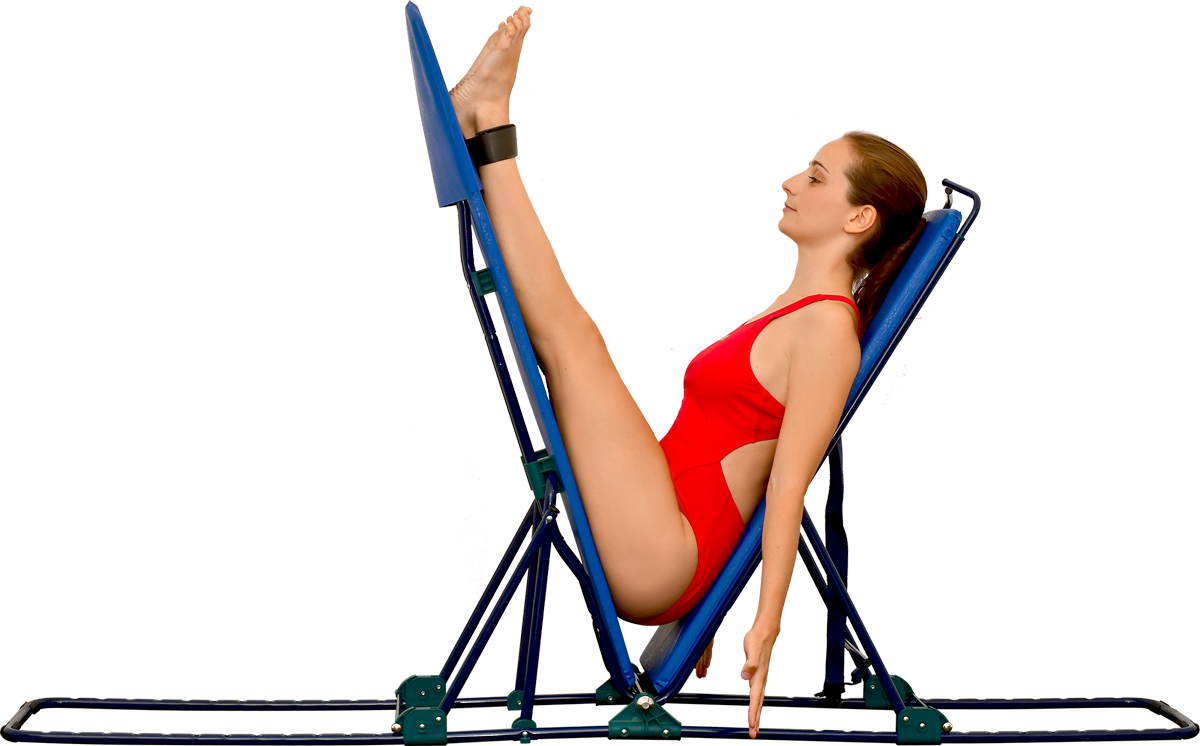
Adjustment of the closing angle of thigh/torso and torso/thigh from 180° to 0°.

Handles on top of the seatback allow to stretch upper limb muscles while maintaining an exact alignment with the torso.
KEY FACTSThe Global Stretching Method
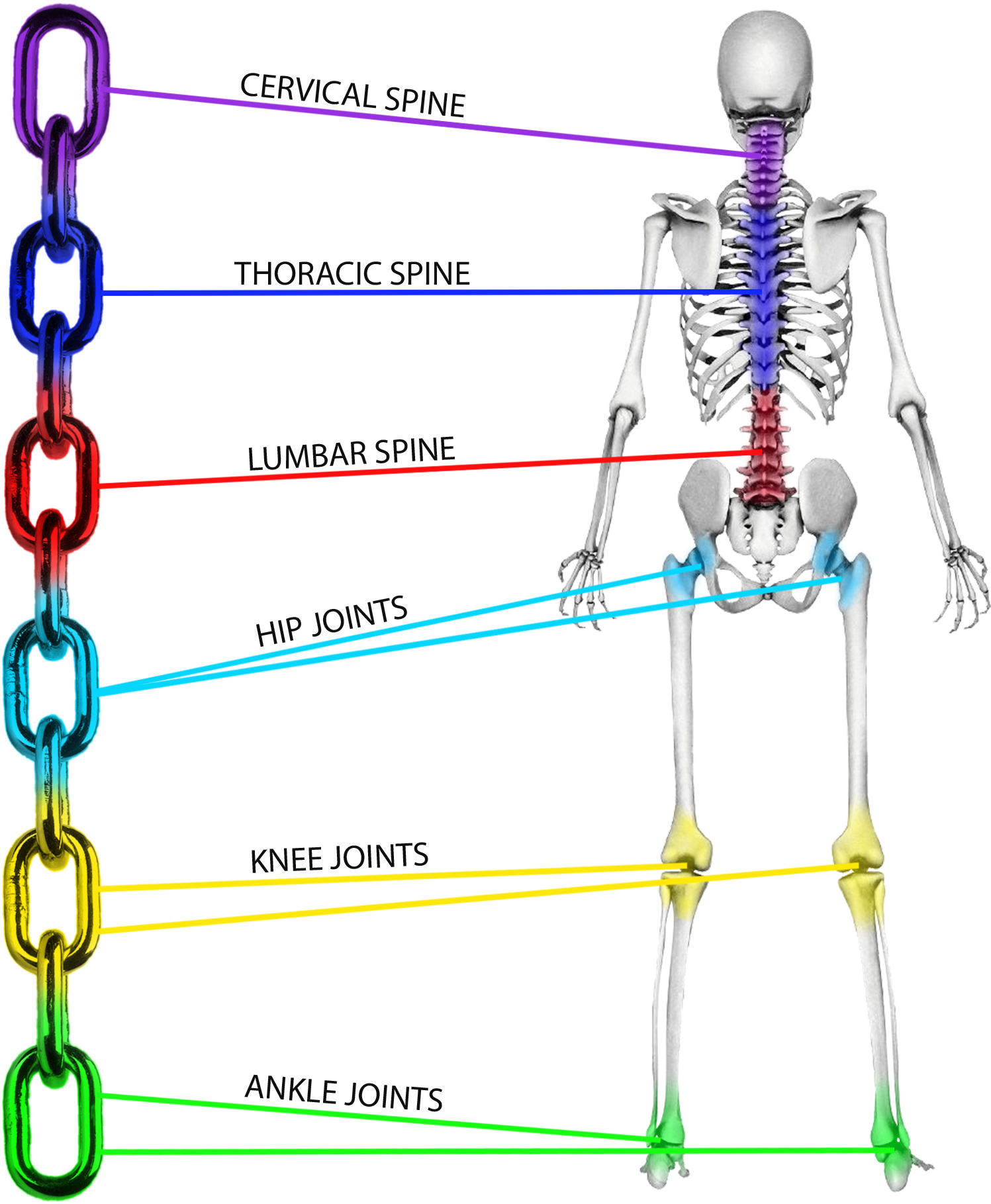
1. Muscular Chains – What are they?
Each muscle represents a link in a chain. Working on a single muscle is somehow limited and less efficient unless this specific muscle is related and connected to its whole chain, and that chain to other chains.
The resistance of a chain is determined by its weakest link; often enough, it is hidden behind balance mechanisms activated by the body, thus compromising its flexibility while overloading some articulations.
Recent and past traumas dissolve into the body leaving faulty postures which, in turn, hinder its full functional expression and muscular and motor development.
Global decompensated stretching, according to a prior individual analysis carried out for each patient, allows to:
– Spot weak links while stimulating and promoting their correction;
– Integrate a single link into the whole system;
– Reprogram movements from a neurologic viewpoint so as to eliminate all traces of previous postural flaws.
2. The importance of coordination in breathing
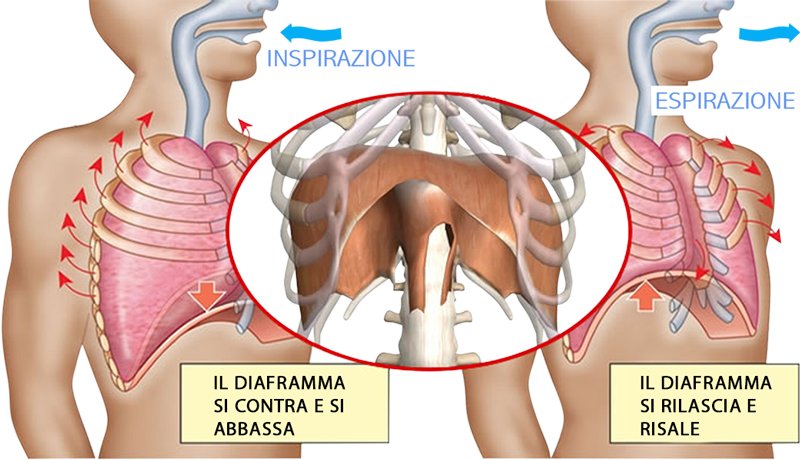
Breathing rhythm is life rhythm: a correlate study of respiratory rate/breathing depth, muscular coordination and rhythm allows to gather many important postural data for each individual.
In Global Stretching, the breathing rhythm is mainly used as endogenous engine for the body, that is, the engine that articulates both the muscular toning phase (inhaling) and the muscular releasing phase (exhaling). By enhancing a slow, passive and deep exhalation, the whole muscular chain system can better receive and absorb the stretching stimuli that it undergoes.
From a biomechanics viewpoint, the diaphragm (the main breathing muscle) represents the key link of all muscular chains. When properly stimulated in a physiological correct way, it allows to reach all the deepest and usually inaccessible muscular chain links, thus leading to their better neurological reprogramming.
3. Body parts control to induce effective stretching
Subtle and precise movement management of body articulations is necessary to efficiently stretch the whole chain and to obtain a deeper neuromuscular reprogramming.
Chain extremities (feet, hands, head and tongue), or end links, are extremely important for proprioception and body balance-related goals.
Each of these end links requires a precise and extreme level of control. For each of them there are specific protocols and workouts to be followed in order to achieve the next level of performance.
4. The importance of planning
During the year, each athlete’s training is scheduled on the basis of the annual competition program. Stretching must be planned too, thus allowing the body to gradually set up, recover and take advantage of a greater performance capacity (supercompensation).
It is important to monitor each athlete’s improvements while optimizing times and benefits.
Scheduling can be on a daily, weekly, monthly, yearly basis.
This does not mean to alter the athlete’s routine, but to implement new, specific and targeted exercises/workouts, and to take advantage of the full potential of each exercise being performed while carefully paying attention to its details.
5. How to Implement Global Stretching
Each athlete learns the difference among various stretching routines/workouts, according to the goals to be achieved. Individual athletes have their own specific needs, so functional and targeted stretching can be useful to fulfil them.
- Post-training release phase: soft prolonged stretching, with an emphasis on both diaphragmatic and chains release/deactivation.
- Technical gesture fine-tuning: medium intensity stretching targeted to specific joints involved in each gesture biomechanics. To be paired with proprioceptive exercises.
- Prevention: soft global decompensated stretching and functional improvement of proprioceptive systems.
- Therapy: in case of injuries or post-traumatic recovery. Individual treatment with a professional osteopath is highly recommended. Extreme care should be taken in considering strengthening exercises/workouts; global muscular decompensated rebalancing is the preferred choice.
The Project
Goals
Schedule
This schedule does not necessarily apply to consecutive weeks; the planning is calibrated on the field, in accordance with the team’s rhythm and the specific needs of each athlete.
IMPROVEMENTS